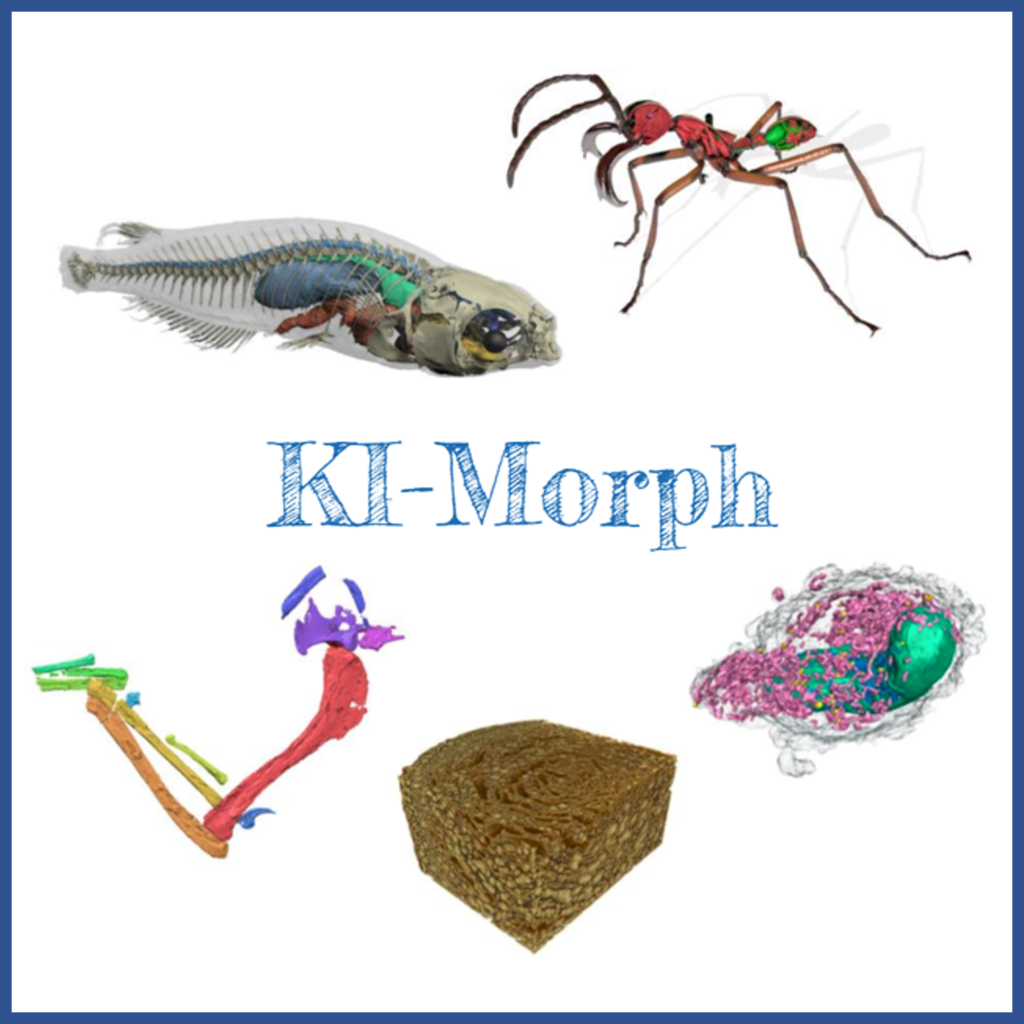

By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence, KI-Morph project automates the segmentation process, saving valuable time and resources while ensuring accurate results.
more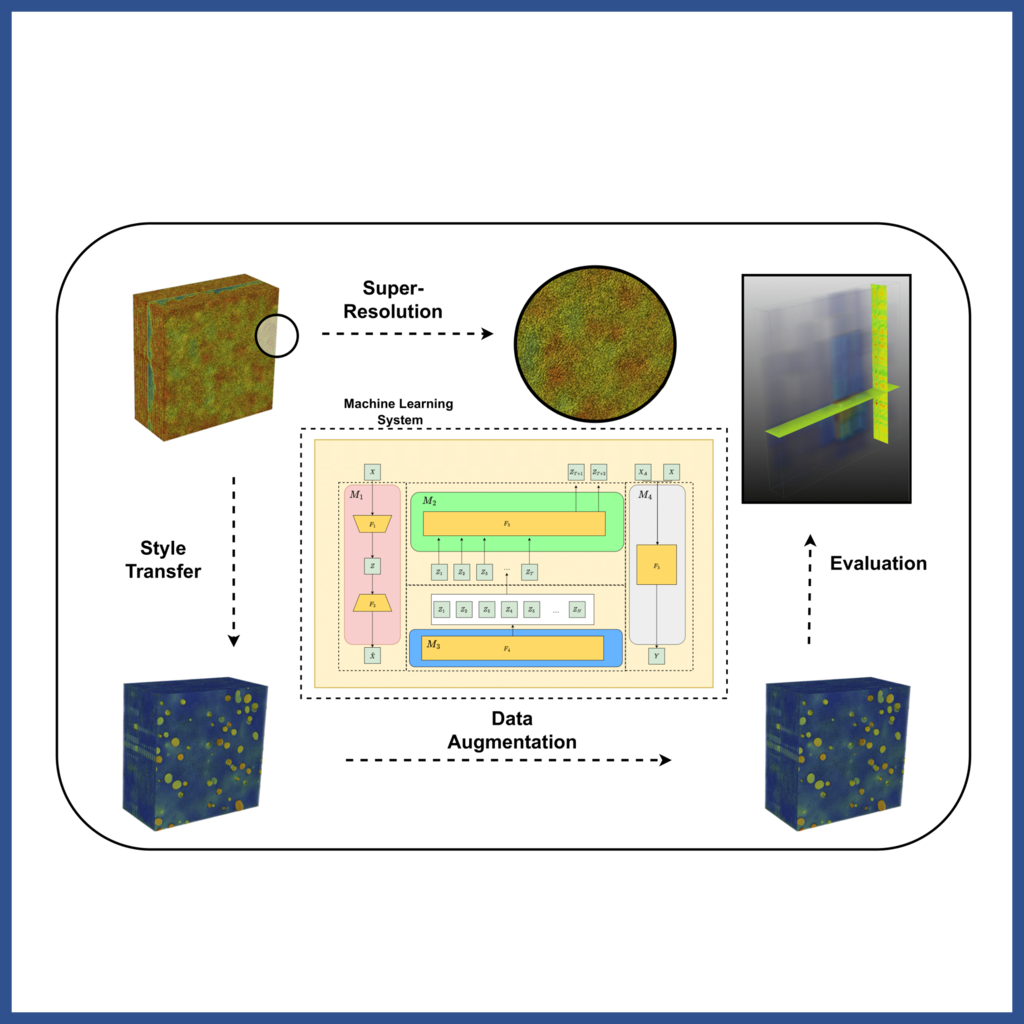
The overall objective of the project is to leverage Artificial Intelligence techniques for more efficient use of synchrotron radiation sources with micro-computed tomography (4D-CT).
more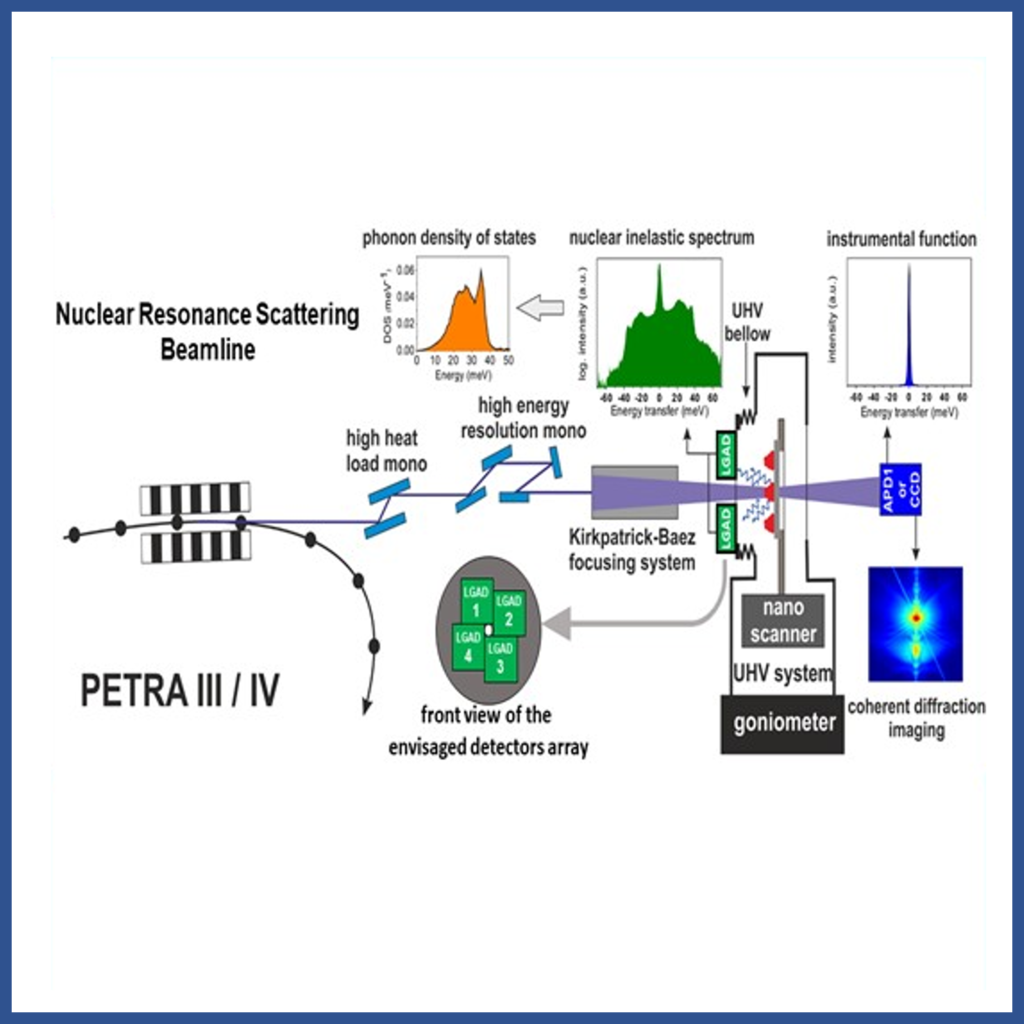
The aim of the LANRS project is to establish nuclear inelastic scattering as a unique experimental method for determination of the lattice dynamics of individual nano-objects using nano-focused x-ray beam at PETRA III/IV.
more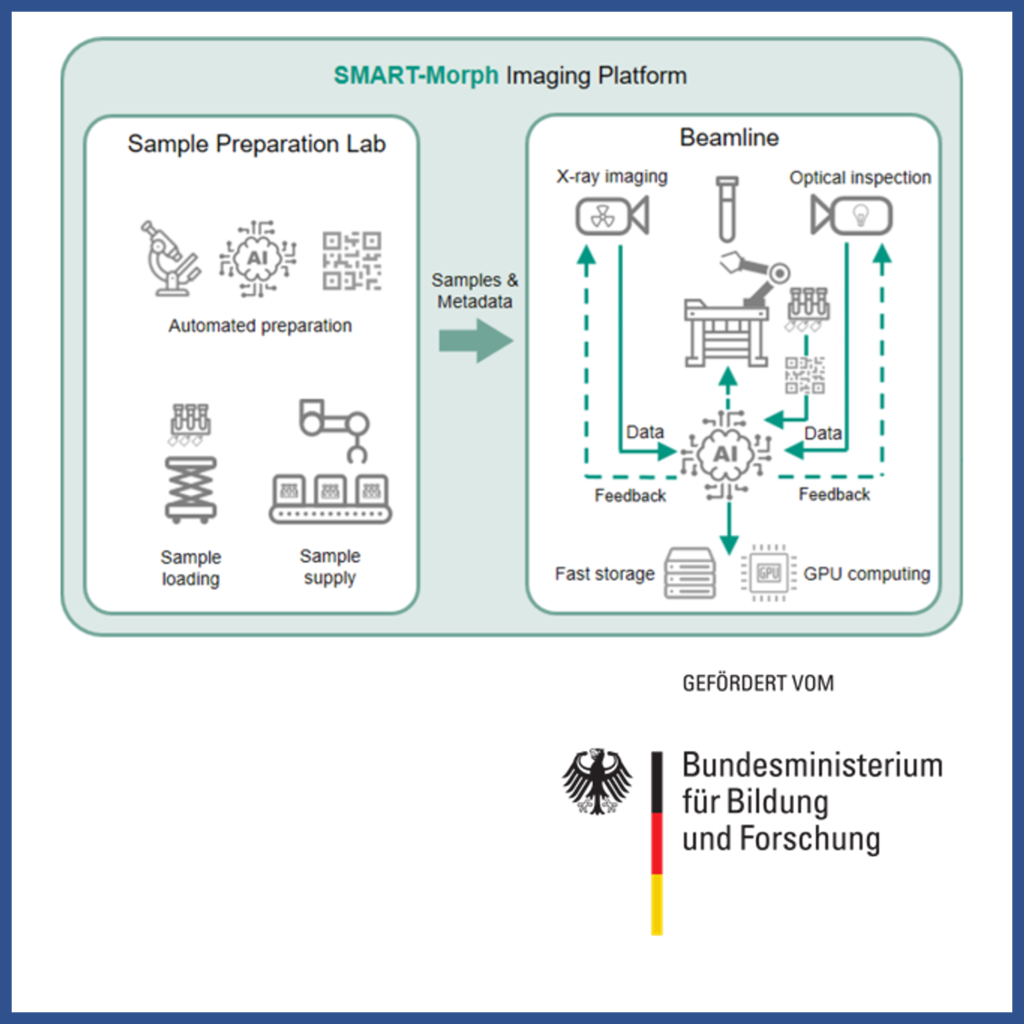
SMART-Morph develops automated, AI-assisted workflows for high-throughput 3D imaging of small organisms using Serial Micro-Computed Tomography (SµCT) at synchrotron facilities. The project enables large-scale morphological studies, linking morphology with molecular and ecological data for diverse scientific applications.
more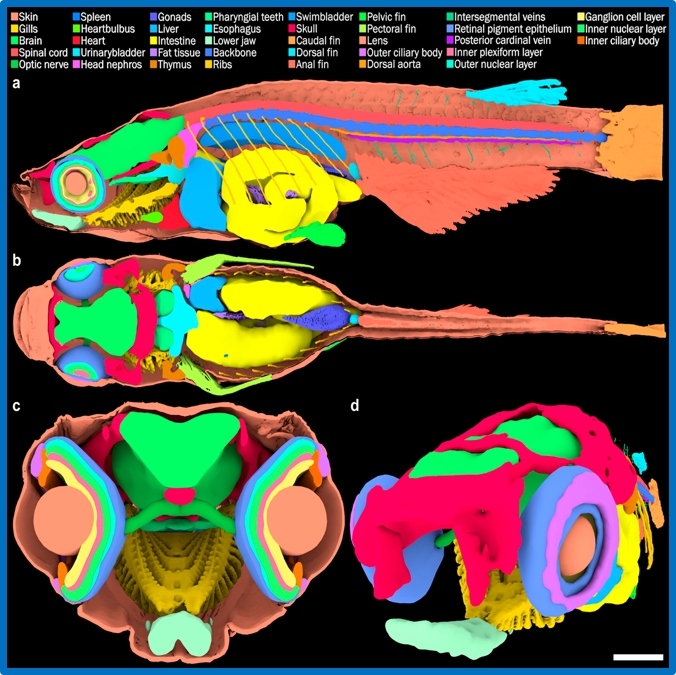
CODE-VITA is a joint project between the University of Heidelberg and KIT (Laboratory for Applications of Synchrotron Radiation) to develop synchrotron measurement technology for dose-efficient X-ray imaging, and to apply this exemplarily for research into development processes in model organisms which are optically opaque and therefore less accessible to visible light optical methods.
more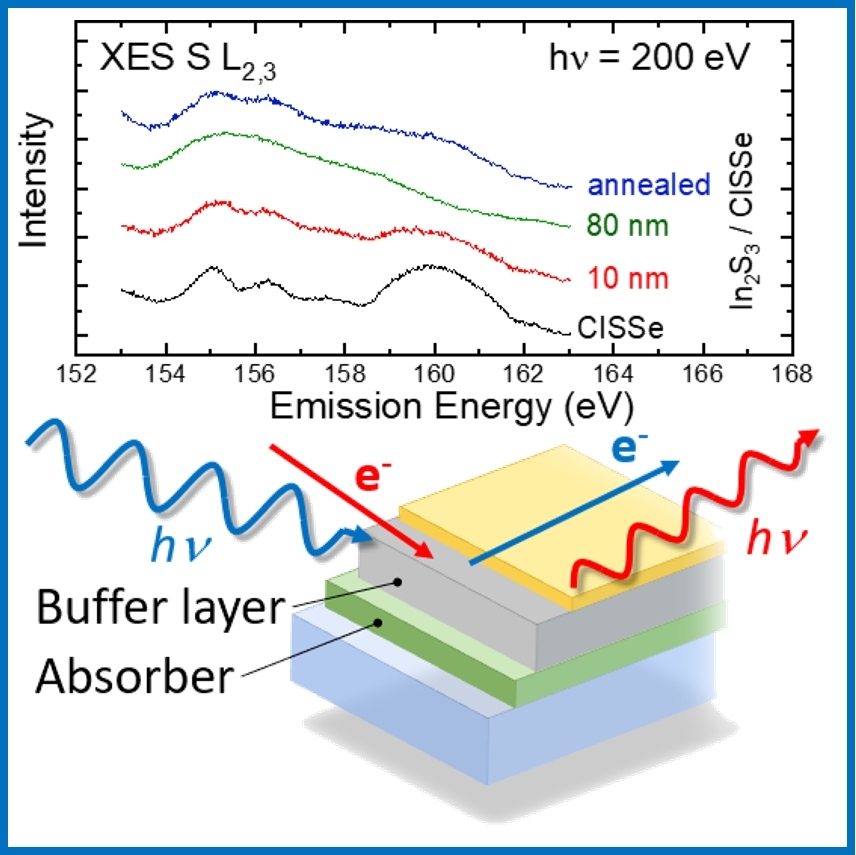
The aim of EFFCIS is to improve the efficiencies of Cu(In,Ga)(S,Se)2 thin-film solar cells and modules via the improvement of the solar cell’s layers and alternative buffer layers. Buffer layers within the CIGSSe absorbers are studied by means of a unique combination of soft x-ray and photoelectron spectroscopies.
more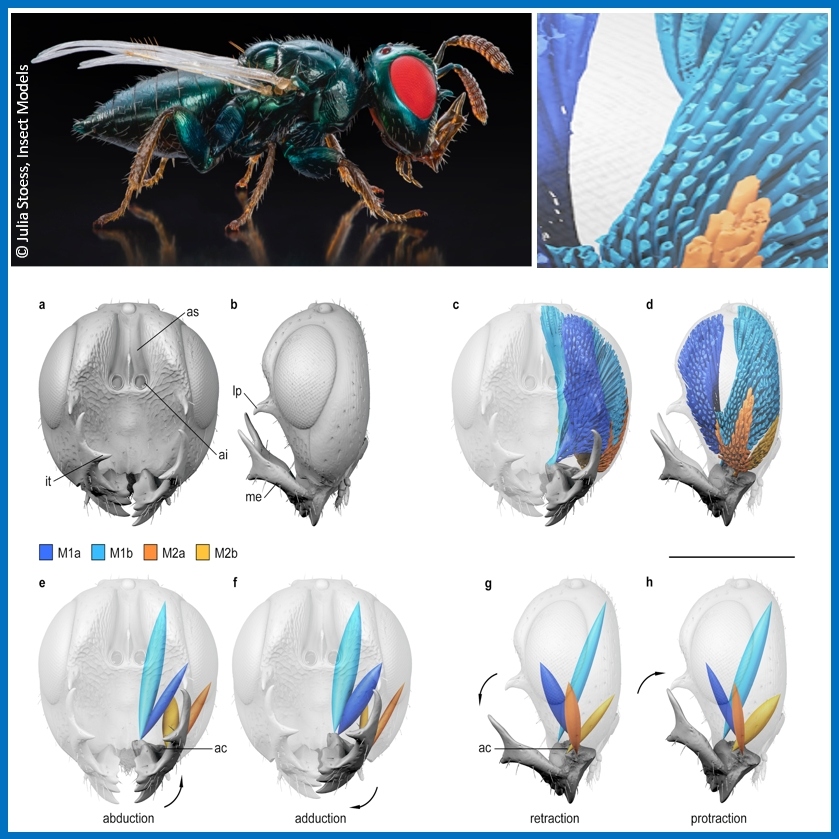
Acquisition of complete 3D morphological information of small animals. The project addresses general requirements in two fields of current biological research: vertebrate model organisms such as fish, frog etc., and arthropods such as insects, which fulfill key functions in our ecosystems.
more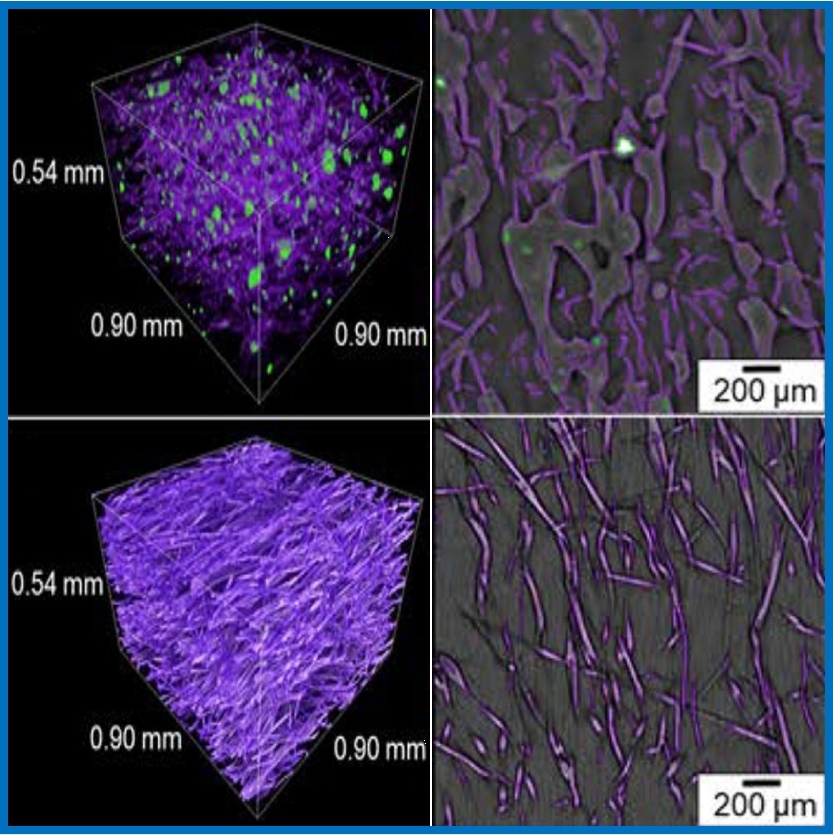
is an interdisciplinary approach to the fabrication and biochemical and biophysical characterisation of three-dimensional hybrid scaffold frameworks with controlled pore-hierarchies for bone-engineering. A key goal is the characterisation of the hierarchical structure of such frameworks by means of 3D X-ray synchrotron imaging techniques.
more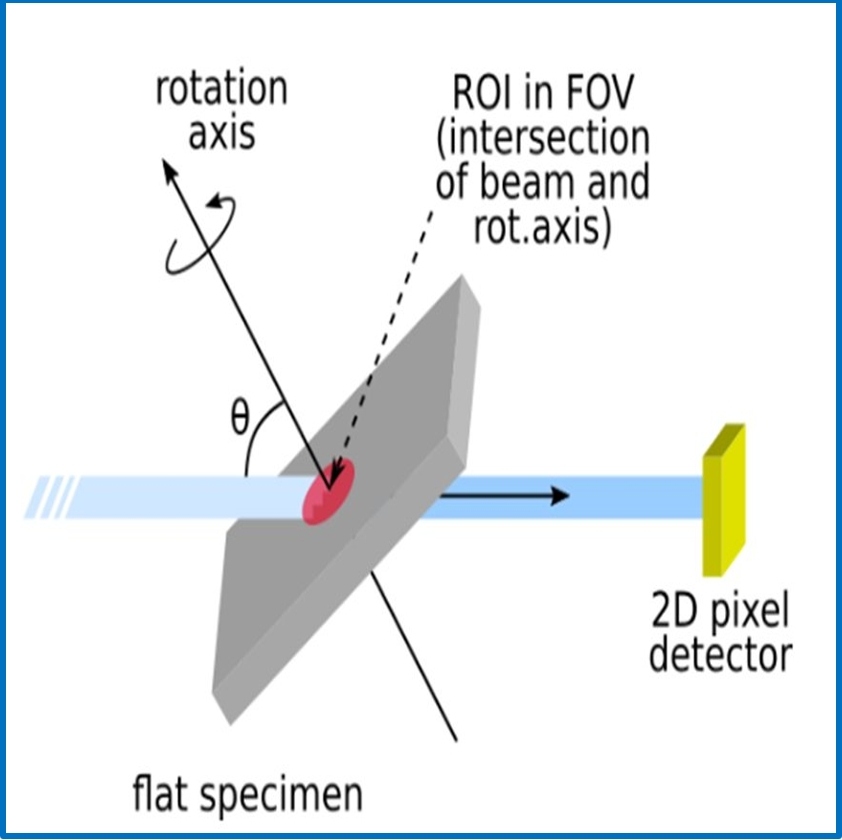
3D imaging of the microstructure inside flat sheet-like materials during testing under bi-axial loading. The methodology allows a unique multi-scale approach from a few hundred micrometers down to nanometer scale to investigate ductile damage nucleation and growth kinetics.
more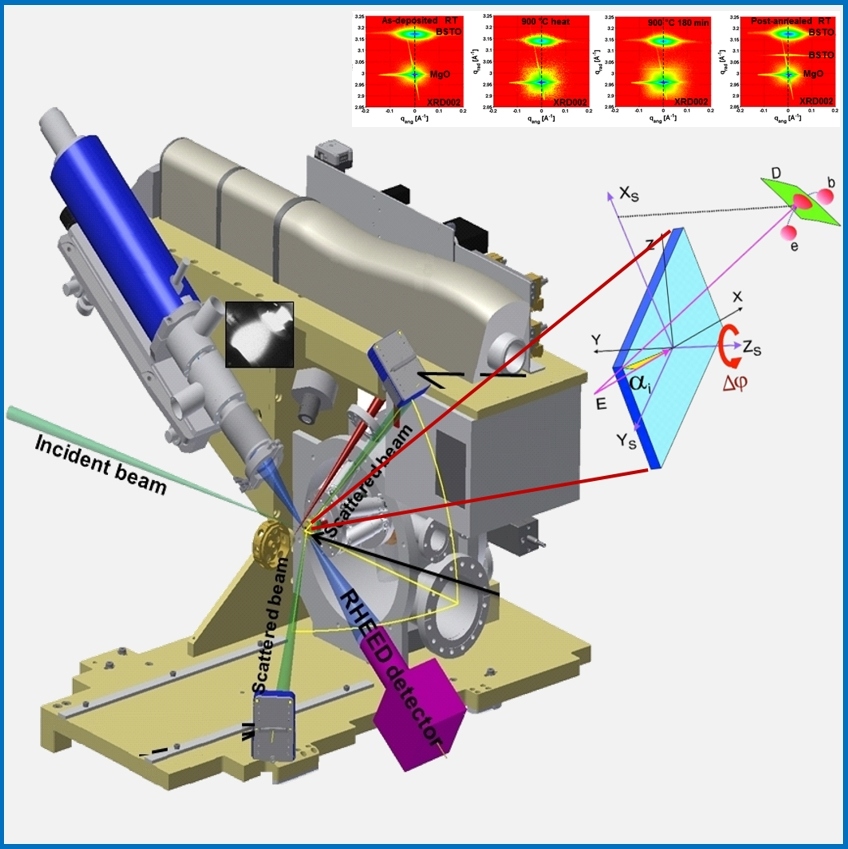
PLDLINK applies in situ X-ray scatttering methods to gain fundamental understanding of the growth of complex oxides produced by pulsed laser deposition (PLD), to enable optimization of the growth parameters for fabrication of multiferroic oxide systems with high technological relevance.
more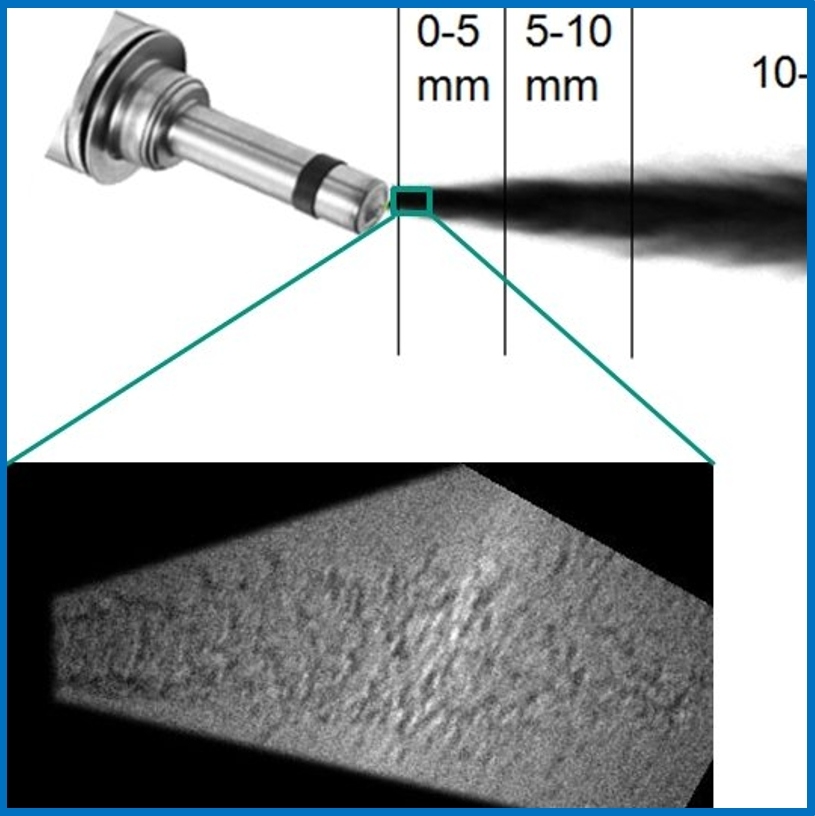
PN-Reduktion applies high-speed X-ray radiography and shadowgraphy to characterize the physical development of fuel spray during its development and to correlate these data to flow-simulation models.
more